Get Equipment
Get your own Ellab equipment to validate, qualify and monitor your processes.
Rent Equipment
Rent Ellab equipment for projects of any size and try our solutions before you commit.
Field Service and Consulting
Get on-site validation, qualification and calibration services as well as expert GMP consulting.
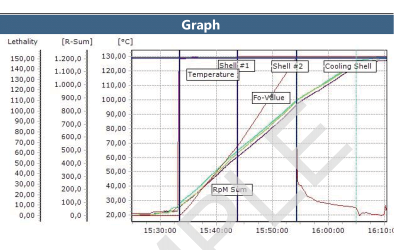
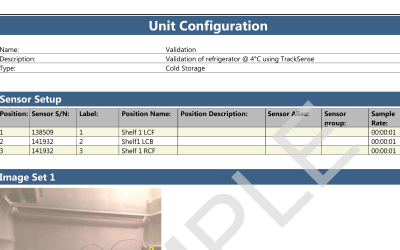
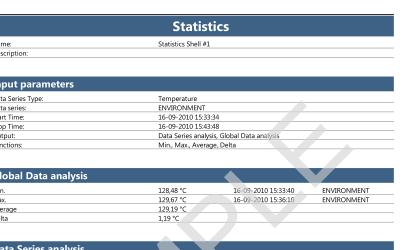
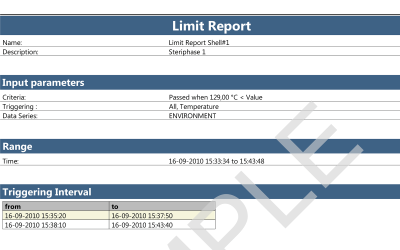
ValSuite® Software Reports
Environmental Testing