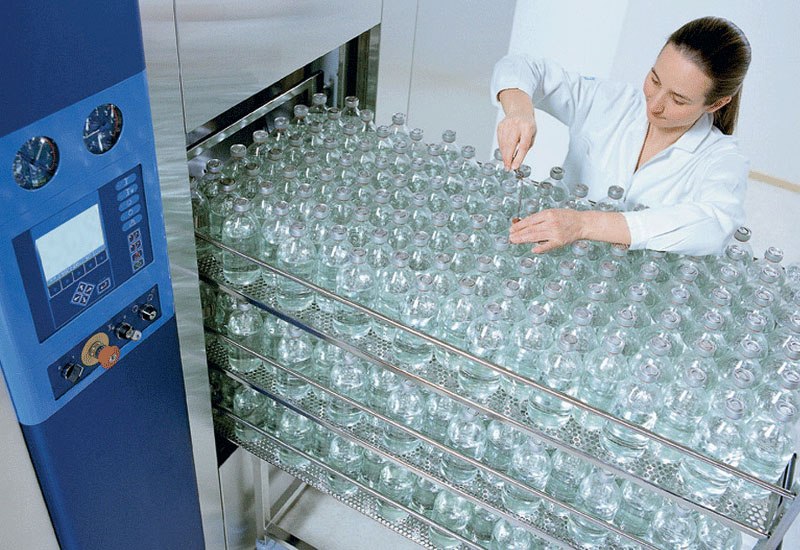
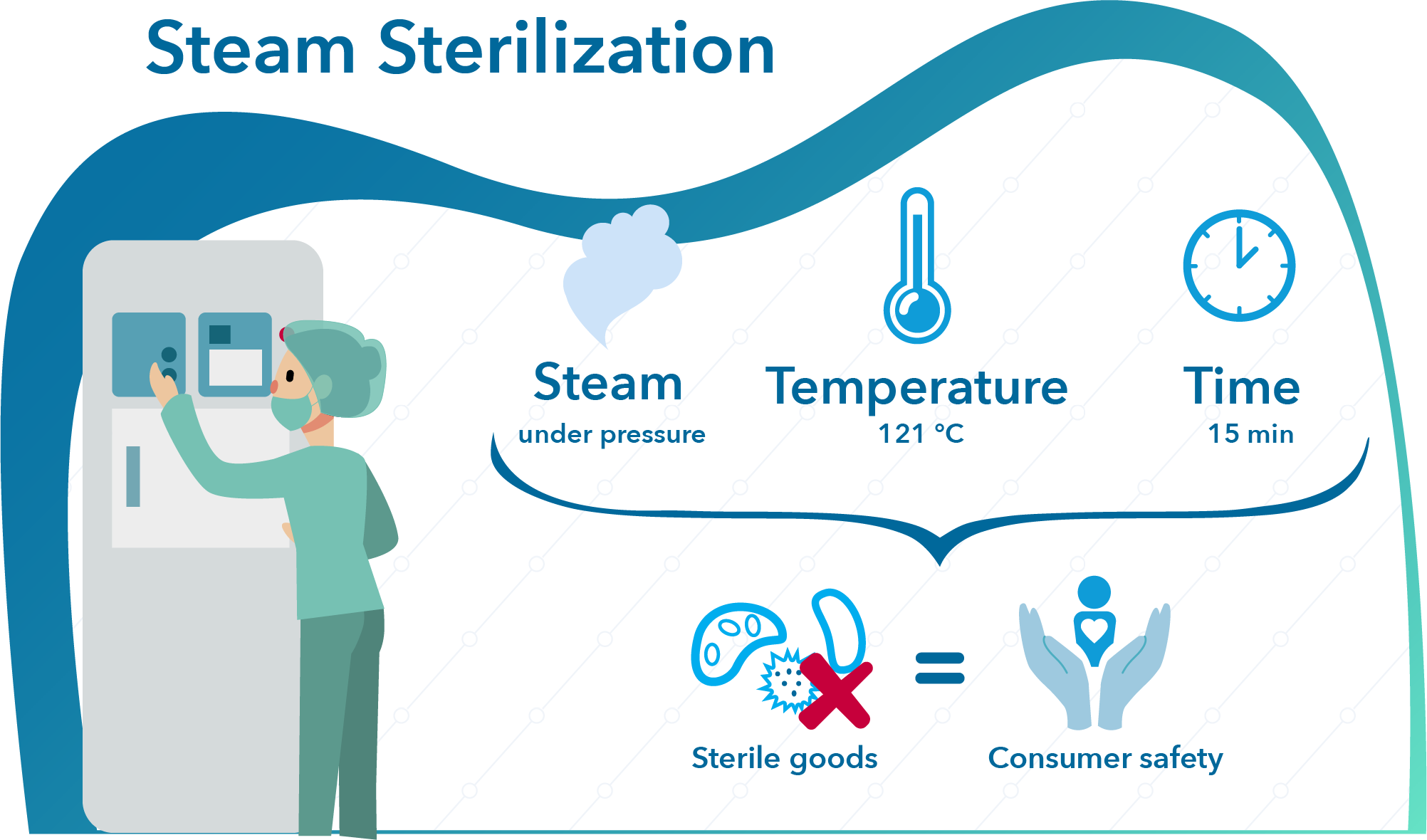
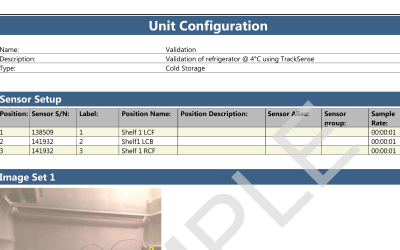
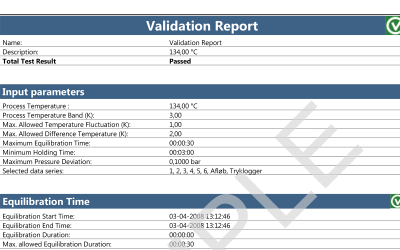
Both wireless data loggers and thermocouple systems are a suitable choice when looking for qualification and/or validation equipment for steam sterilization and autoclaves.
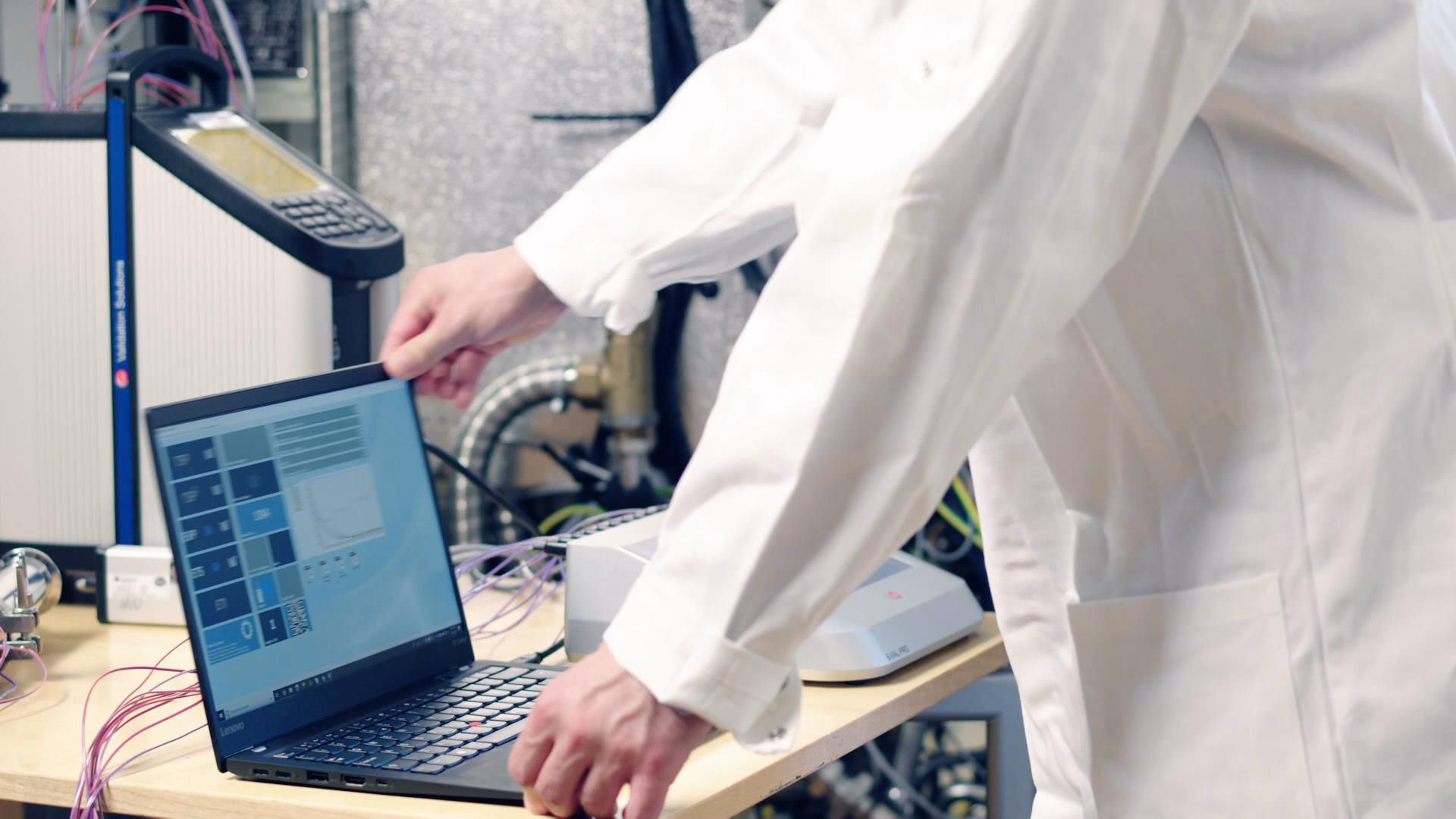
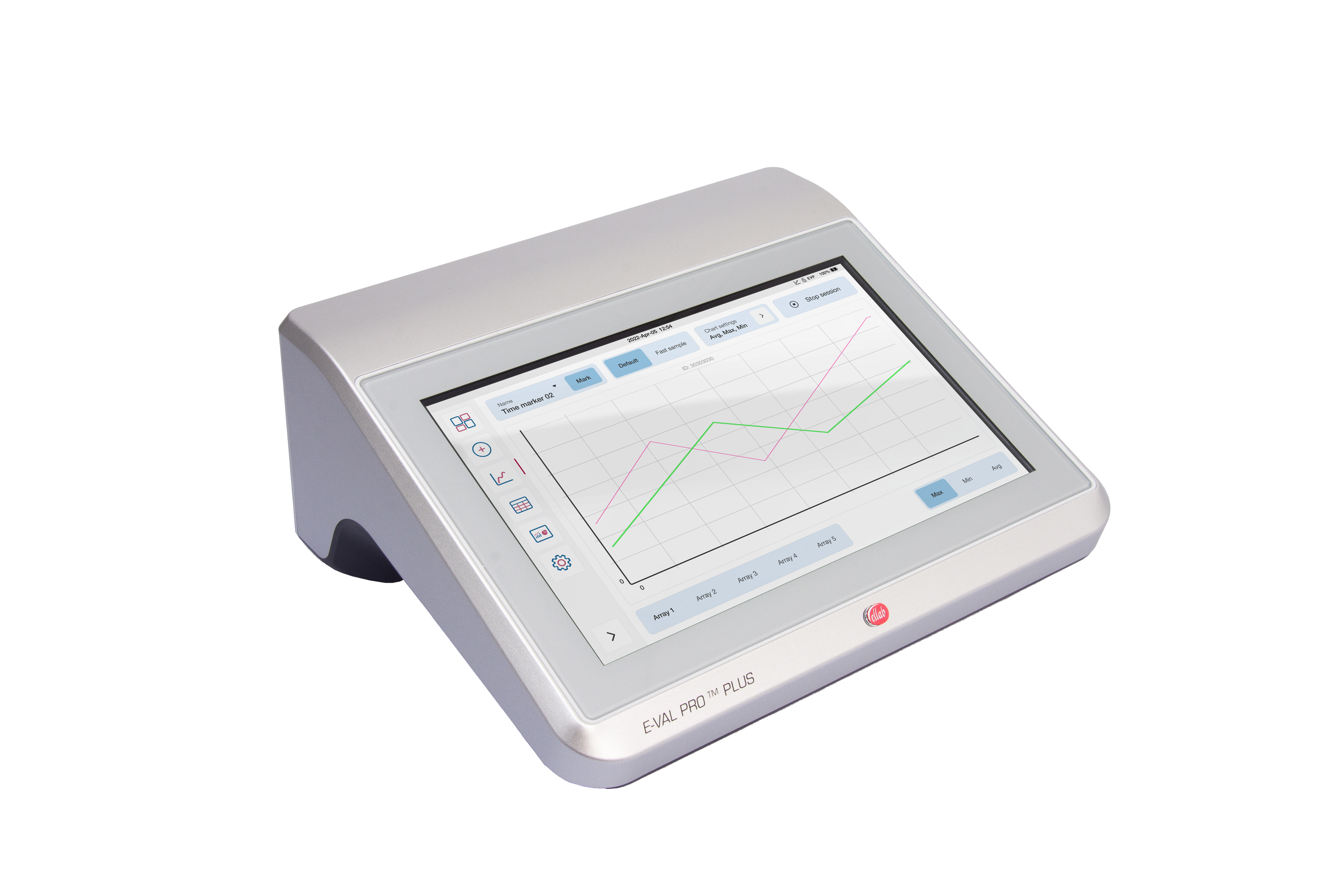
Wireless loggers are, due to the RTD sensor design, very accurate and stable, which makes them the ideal option for both qualifying the autoclave and validating the steam sterilization process.
A wired thermocouple system can also be used and may initially be the more economical option but will ultimately require far more resources to operate – resulting in challenges that could be avoided by using a wireless system. This is due to wireless data loggers being much easier to setup and control when compared to its cabled counterpart.
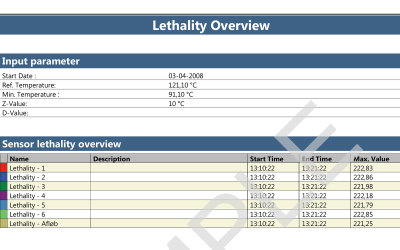
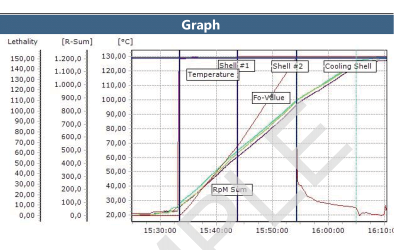
When using a wired thermocouple system for autoclave validation, there is the added challenge of maintaining the pressure and vacuum integrity. This is due to the necessity of using a feed-through system to allow the thermocouples into the chamber. Ellab’s feed-through system has been tested rigorously to ensure minimal leakage and optimal qualification efficiency.