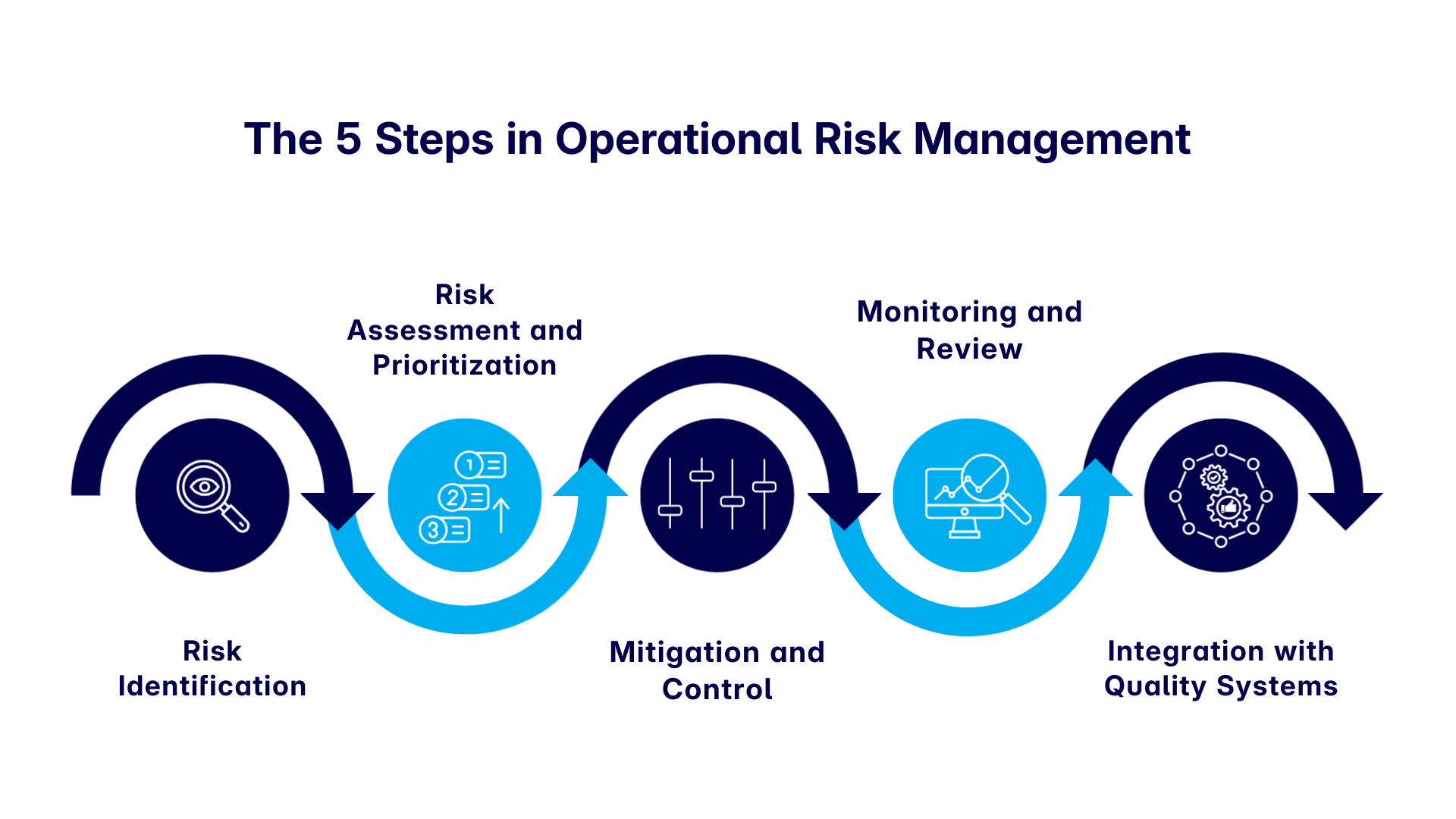
Developing a risk management framework tailored to your operations ensures that compliance efforts are both efficient and scalable. A solid ORM framework typically includes:
1. Risk Identification
In this step, we carefully review all key areas where issues might affect quality or safety, like calibration drift, power loss, process deviation, or alarm fatigue. This helps us ensure everything runs smoothly and safely.
Tools such as Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and structured walkdowns can help teams proactively uncover vulnerabilities. Reviewing CAPA history and audit findings further highlights areas with recurring or latent risk.
2. Risk Assessment and Prioritization
The second step focuses on evaluating the probability and impact of identified risks. Tools such as risk control self-assessments, key risk indicators (KRIs), and incident management systems play a vital role here.
KRIs should be tied to measurable metrics, like alarm response times, calibration percentages, or deviation frequency, and scored using the standard ‘Severity × Occurrence × Detectability’ model. In addition, organizations should define their risk appetite, clarifying which risks demand immediate attention and which can be tolerated. This structured approach ensures risks are prioritized effectively.
3. Mitigation and Control
Once risks are prioritized, take steps to implement preventive, detective, and corrective actions:
- Preventive: Measures such as environmental monitoring systems (EMS), calibration programs, and UPS power backup.
- Detective: Alarms, audit trail reviews, and trending analyses to identify issues before they escalate.
- Corrective: CAPAs, supplier fixes, and change control to remediate deviations and strengthen future resilience.
Leveraging advanced tools like an environmental monitoring system can be a great way to spot out-of-spec conditions in real time, helping to lighten the manual workload and improve data integrity and real-time visibility into operations.
4. Monitoring and Review
Risk management is not a “set and forget” process; it requires continuous oversight. Establish and track KPIs/KRIs linked to compliance and performance, such as alarm response times, calibration percentages, and CAPA recurrence rates. Make sure to review these metrics regularly so you stay up-to-date with operational changes and the evolving regulatory landscape. This proactive monitoring keeps your compliance program aligned and audit-ready.
5. Integration with Quality Systems
Finally, a strong ORM framework should be seamlessly embedded within your Quality Management System (QMS). This integration should guide decisions not only across CAPAs, deviations, SOPs, and training, but also include change control, document control, and supplier quality processes. By aligning ORM with QMS elements, you create a unified compliance ecosystem that ensures risk awareness and accountability across your entire operation.